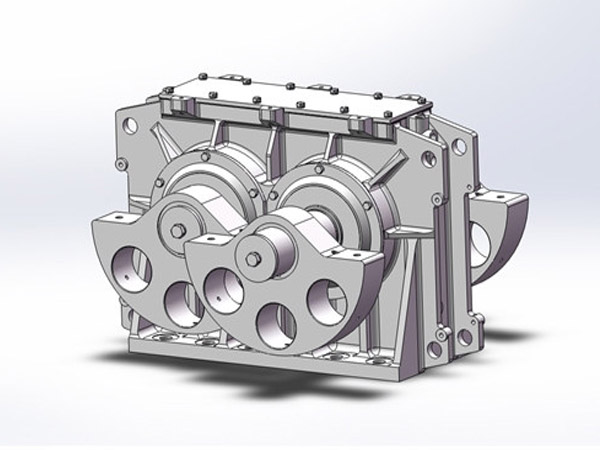
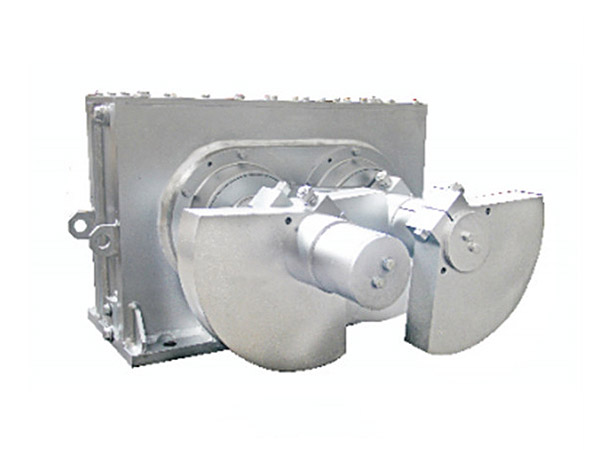
Vibrating Screen Exciter Guide: Design, Key Components, and Performance Optimization Tips
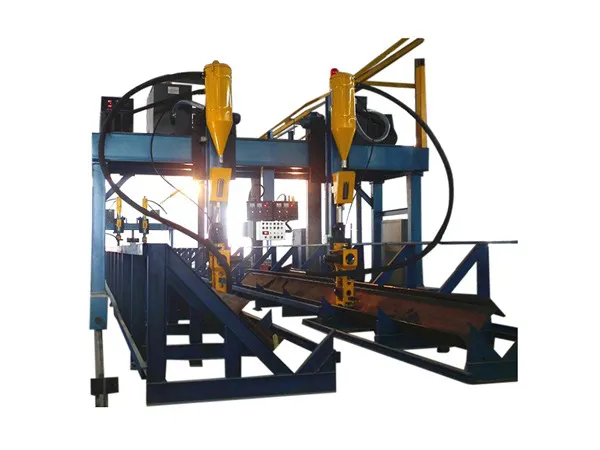
The vibrating screen exciter is the core of any screening system. It generates the vibration force needed to move materials across the screen surface, directly affecting efficiency, throughput, and machine lifespan. A high-quality exciter ensures stable performance, reduced maintenance costs, and improved product quality.
This guide covers key components, structural design considerations, and optimization strategies to help engineers, plant managers, and buyers make informed decisions.
What Is a Vibrating Screen Exciter?
A vibrating screen exciter (also called an exciter unit) is a mechanical device that converts rotational energy into oscillations required for effective material screening. It is widely used in:
Mining and mineral processing
Aggregates and construction materials
Coal preparation
Metallurgy
Chemical and recycling industries
A well-designed exciter ensures stable vibration amplitude, balanced force output, and consistent screening efficiency.

Key Components of a Vibrating Screen Exciter
Understanding core components is essential for selection, operation, and maintenance:
1. Housing / Exciter Body
Supports bearings, shafts, and gears
Made from high-strength steel or cast alloy
Precision machining ensures stable vibration
2. Shaft(s)
Single or dual shaft depending on design
Transmits rotational force
Heat-treated to withstand heavy cyclic loads
3. Bearings
Heavy-duty spherical or cylindrical roller bearings
Designed for high-speed rotation and vibration stress
Bearing quality directly impacts exciter lifespan
4. Gears
Synchronize shaft motion
Ensure accurate vibration amplitude and direction
5. Lubrication System
Oil or grease-based depending on design
Prevents premature wear and overheating
Critical for long-term reliability
Structural Design Factors Affecting Exciter Performance
Several structural elements influence exciter performance. Optimizing these ensures higher efficiency, lower downtime, and longer equipment life.
…
For more detailed information on the structural design of vibration screen exciter guidelines, please click to visit: https://www.hsd-industry.com/news/vibrating-screen-exciter-structure-design/